API Requests in Postman
Postman is a graphical tool for building, sending, and debugging API requests without writing code. You can use it to explore the DIDWW API, inspect responses, confirm your API keys, and prototype integrations before adding them to your application.
Before You Begin
An active account with DIDWW is required. Create Your Account .
Create at least one active API key in the DIDWW User Panel. See Create API Key.
It is recommended to install the Postman application. Download Postman .
Sign in to an active Postman account. Create an account .
Step 1: Fork the DIDWW API Collection
Create a personal copy of the official DIDWW API collection in your Postman workspace so you can edit and test the requests.
Open the DIDWW Workspace
Open the official DIDWW API Postman Workspace .
If you are not already signed in, Postman will prompt you to log in.
Fig. 1. Postman sign-in screen.
Fork the Collection
In the left sidebar, locate the latest DIDWW API3 collection version.
Click the Actions (···) button next to the collection name and choose Fork to create a personal copy in your workspace.
Fig. 2. Actions and Fork Button.
Enter a Fork label and select your Workspace.
(Optional) Select the Environment to fork or configure the environments later.
(Optional) Enable Watch original collection if you want to be notified about changes to the original collection.
Click Fork Collection.
Fig. 3. Forking the collection into your personal workspace.
Open the Collection in the Postman Application
Open the Postman App. Your personal copy of the collection appears automatically.
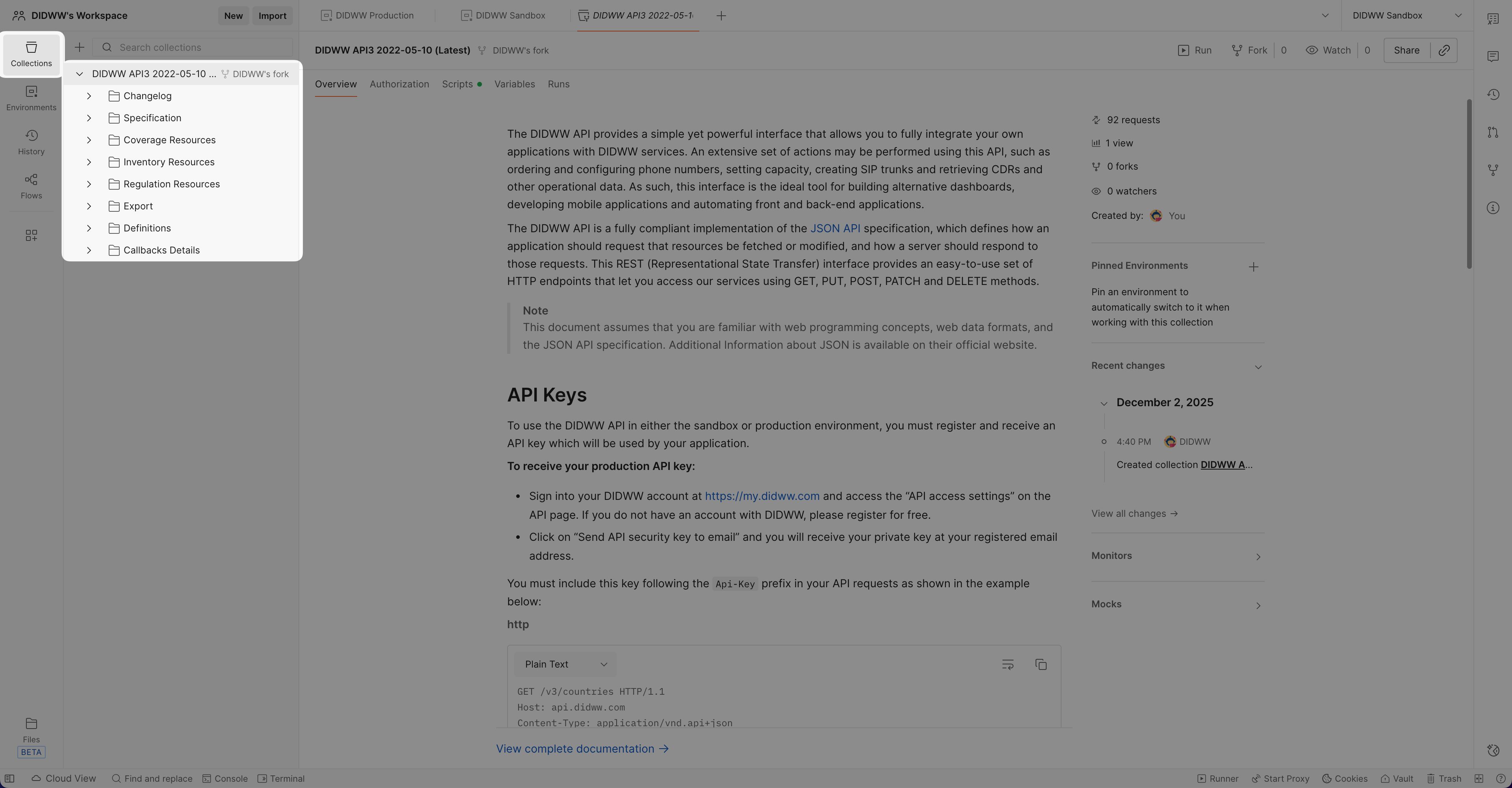
Fig. 4. Forked collection in the Postman App.
Step 2: Configure Environments
Use Postman Environments to store the hostname and API key for each API mode. This helps you switch between production and sandbox environments safely and reduces the chance of using the wrong API key or host.
Configure the host and apiKey variables for the Sandbox API.
Configure the host and apiKey variables for the Production API.
Configure the Sandbox Environment
Click on the + symbol to the left of the Search environments bar to create another environment.
Name it, for example: DIDWW Sandbox.
Add the following variables:
Variable
Value
Description
hostsandbox-api.didww.comHostname for the sandbox API.
apiKey<YOUR_SANDBOX_API_KEY>Your sandbox API key from the User Panel.
Note
If you do not have a sandbox account or API key, contact support@didww.com .
The DIDWW Postman collection uses
{{host}}to build URLs (for example:https://{{host}}/v3/dids). Enter only the hostname (for example,sandbox-api.didww.com) withouthttps://or/v3.
Fig. 6. Example Sandbox Environment.
Configure the Production Environment
In Postman, go to the Environments tab.
Click the + symbol to the left of the Search environments bar to create a new environment.
Name it, for example: DIDWW Production.
Add the following variables:
Variable
Value
Description
hostapi.didww.comHostname for the production API.
apiKey<YOUR_PRODUCTION_API_KEY>Your production API key from the User Panel.
Note
The DIDWW Postman collection uses {{host}} to build URLs (for example: https://{{host}}/v3/dids). Enter only the hostname (for example, api.didww.com) without https:// or /v3.
Fig. 5. Example Production Environment.
Select the Environment
Click the button to set the correct environment active before sending API requests.
Fig. 7. Switching between Production and Sandbox.
Step 3: Configure Required Headers and Authentication
The DIDWW API follows the JSON:API specification . All requests must include the correct JSON:API headers and your API key.
Note
For more detailed hostnames and authentication rules, see the Getting Started with the DIDWW API and Specification headers sections.
Open a Sample Request
You can use any request in the collection for this step. For example:
In your forked DIDWW API collection, expand the Inventory Resources folder.
Click DID to open the DID resource group.
Select the Get DIDs request.
Fig. 8. Sample DIDWW API request opened in Postman.
Verify the Required Headers
The official DIDWW Postman collection already includes the required headers. Verify that they are present, enabled, and correctly configured.
With the Get DIDs request open, go to the Headers tab.
Ensure that the following headers exist and are enabled:
Header
Example Value
Description
Acceptapplication/vnd.api+jsonRequired for all API responses.
Content-Typeapplication/vnd.api+jsonRequired for all JSON request bodies.
Api-Key{{apiKey}}Authentication header using the
apiKeyvariable from the selected environment.
Warning
Never share your API key in screenshots, code samples, or public repositories. If it becomes exposed, rotate it immediately in the DIDWW User Panel.
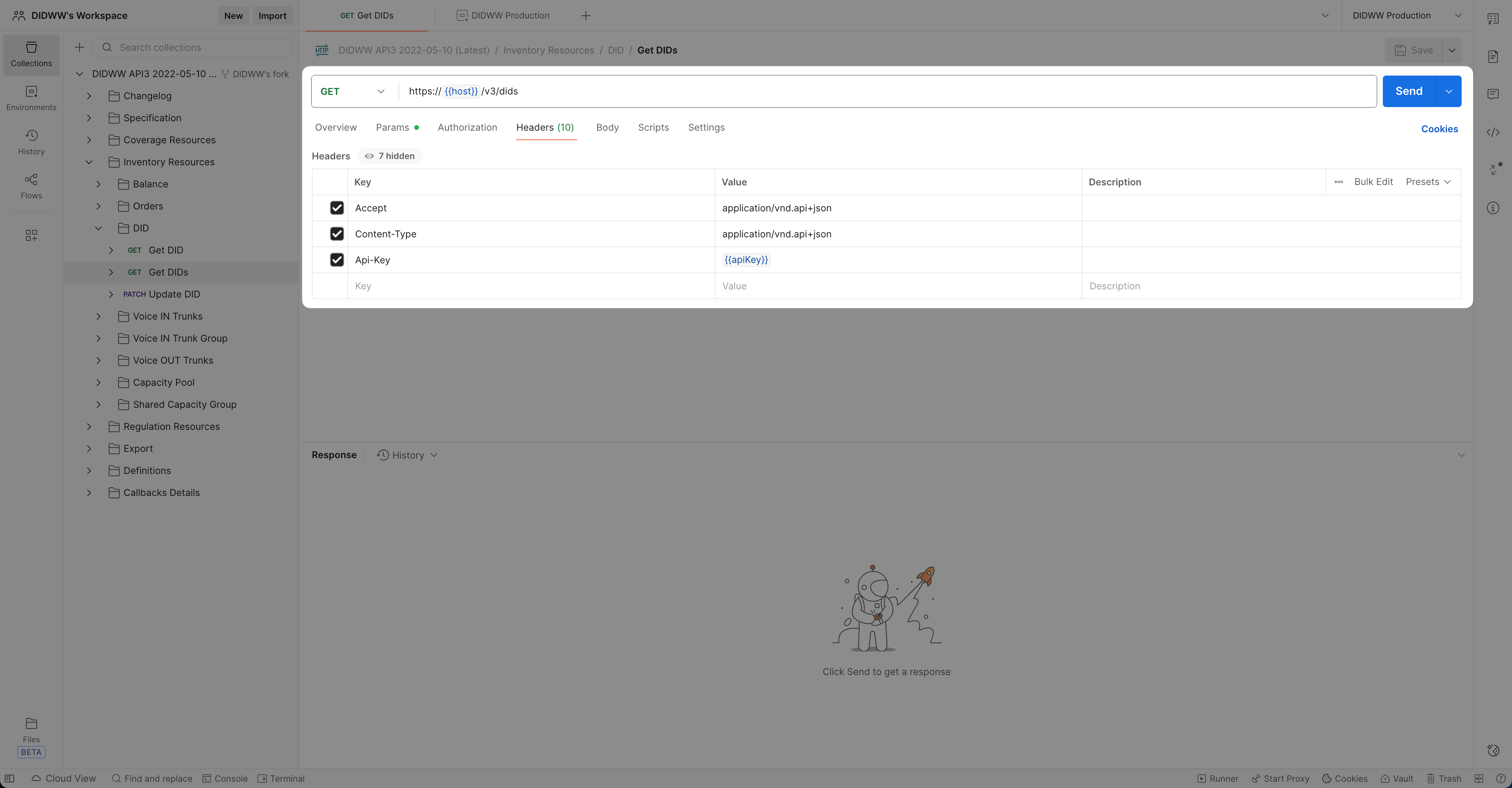
Fig. 9. Sample DIDWW API request opened in Postman.
Step 4: Send Your First Request
When the environment and headers are configured, you can send any request from the collection.
Open a request of your choice (for example, Get DIDs).
Make sure the correct environment is selected.
Click Send.
Fig. 10. Sending a test request in Postman.
Step 5: Check the Response and Troubleshoot Errors
After you send a request, the response appears in the lower Postman panel. Here you can review the status code and the JSON response body.
Success Response
A valid, authenticated request returns a 200 OK status and a JSON response.
Fig. 11. Successful API response.
Troubleshooting API Errors
- 401 Unauthorized
Api-Keyis missing or invalid. Set theapiKeyvariable correctly in the active environment.- 406 Not Acceptable
The
Acceptheader is incorrect. Set it toapplication/vnd.api+json.- 415 Unsupported Media Type
The
Content-Typeheader is missing or incorrect. Set it toapplication/vnd.api+jsonfor any request with a JSON body.- 404 Not Found
The host, endpoint path, or resource ID is incorrect, or the API key does not match the selected host. Make sure
{{host}}is exactlyapi.didww.comorsandbox-api.didww.com(withouthttps://or/v3) and verify the request URL.- 422 Unprocessable Entity
The request body is missing required fields or is not valid JSON:API. Ensure POST or PATCH requests follow the JSON:API document structure. See: JSON API specification